Post written by Office of Environmental and Energy Coordination's Energy Programs Team
Electricity provides lighting around the clock; heats and cools our homes and businesses; and fosters the digital world that we've come to rely on throughout each day.
But where does electricity come from, how is it made and why does it matter?
The Journey of Electricity
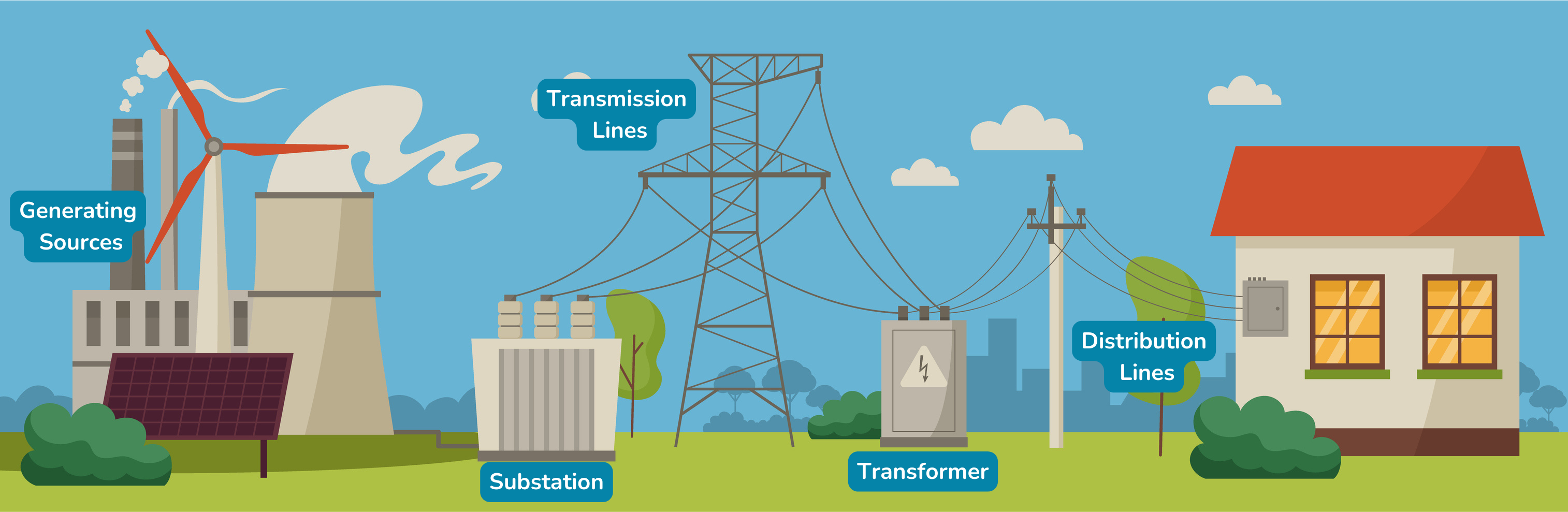
Electricity is a secondary source of energy, which means a primary source of energy, like natural gas, nuclear, sunlight, wind, oil or coal, is converted into electrical power. Traditionally, electrical power has been generated in a power plant. There, primary sources like coal, natural gas, or nuclear are used to create steam, which moves a turbine within a generator to convert kinetic energy – or the energy of motion – into electricity. Renewable energy, such as solar or wind, is not created in a traditional power plant. While wind energy still utilizes a turbine to create power, solar energy utilizes solar photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight directly into electricity.
In Fairfax County, most of the electricity we consume is transmitted and distributed by Dominion Energy. This electricity is generated outside of Fairfax County and moves through a complex system of substations, transformers, and powerlines – sometimes called “the grid” – to us.
Generating Clean Electricity
The source of electricity generation is important for one main reason: some primary energy sources cause a lot of pollution while others are much cleaner. Fossils fuels, such as coal, petroleum, and natural gas, produce large amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions when they are burned to create electricity. Renewable sources, on the other hand, produce almost no emissions. As a secondary source, all electrical energy goes to “the grid” and is made available to all users: we cannot pick electricity generated from a specific source to be used for a specific purpose once it is added to “the grid”.
There are options for getting more of our electric power from less carbon intensive sources. This includes marketplaces for Renewable Energy Credits, and policies like the Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit and the Virginia Clean Economy Act of 2020 (VCEA).
Because of these efforts (and changing prices for primary fuels), we’ve seen a shift in the primary sources used by Dominion Energy. In 2022, Dominion generated its electricity from nuclear (43%), natural gas (41%), coal (11%), petroleum (<1%) and renewable sources such as solar and wind (5%), whereas generation in 2005 came from similar sources but in different quantities: coal (47%), nuclear (44%), petroleum (4%), natural gas (4%), and renewable sources (1%).
If Dominion meets the Renewable Energy Portfolio Standard (RPS) adoption schedule outlined in the VCEA, Fairfax County could receive electricity generated from 100% renewable sources by 2045!
Learn More
For more information on this topic, check out some of the data and metrics on our Energy Supply Metrics page.
Climate Matters is the blog of Fairfax County’s Office of Environmental and Energy Coordination, where we share stories, insights and information related to climate change and environmental sustainability. Posts are written by knowledgeable and passionate OEEC staff members and guest authors. To read all blog posts, visit Climate Matters.

