Tuberculosis (TB) is still a public health problem in Northern Virginia. But TB can be treated and cured!
- Learn more about TB infection and disease.
- Know your risk now.
- Prevent TB: Get tested. Complete treatment.
- Talk to your health care provider or local health department today.
What Is TB and How Do I Get It?
TB is a disease, caused by bacteria, that can spread from one person to another. Most often TB affects the lungs, but you can find it in any part of the body.
TB bacteria are spread through the air in tiny droplets when a person who is sick with TB in their lungs coughs, sneezes or speaks.
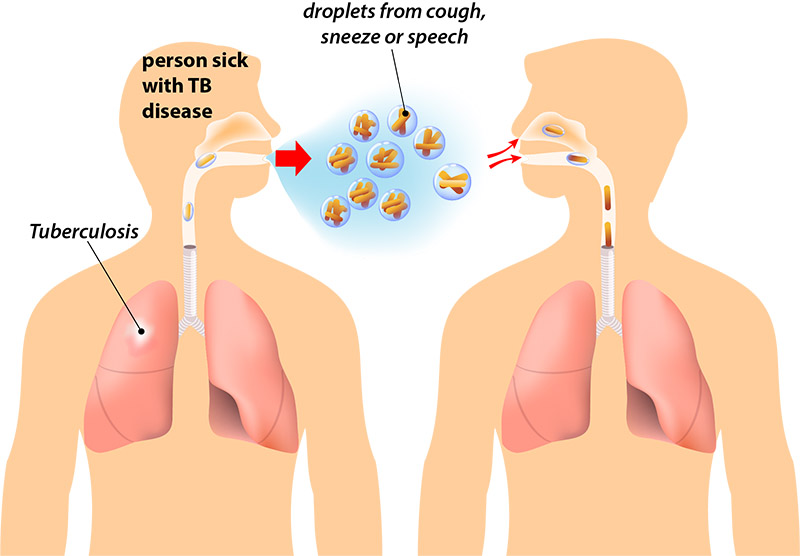
If you breathe in these droplets, you may become infected with the TB bacteria without knowing it because you will not feel sick and will not have symptoms. This is called latent TB infection (LTBI). Millions of people in the United States have TB infection, and without treatment, they are at risk for developing TB disease. That is why getting tested and taking medicine for prevention is important.
![]()
![]()
Image credit: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
What Are the Symptoms of TB?
Symptoms of active TB disease may include:
- Cough lasting three or more weeks.
- Coughing up blood.
- Losing weight.
- Night sweats.
- Fatigue.
- Fever.
Remember, people with latent TB infection do not feel sick and do not have any symptoms.
Who Is More Likely to Become Infected With TB?
If you have one or more of the following risk factors, you have a greater chance of getting TB infection:
- Lived or spent time in a country where TB is common.
- Lived or spent time with someone with active TB disease.
- Lived or worked in a congregate setting (such as a shelter, jail, long-term care or assisted living facility).
- Worked in a health care setting.
- Homeless, especially within the last two years.
- Drug user.
- Infant, child or adolescent who has spent time with an adult at increased risk for TB infection or TB disease.

